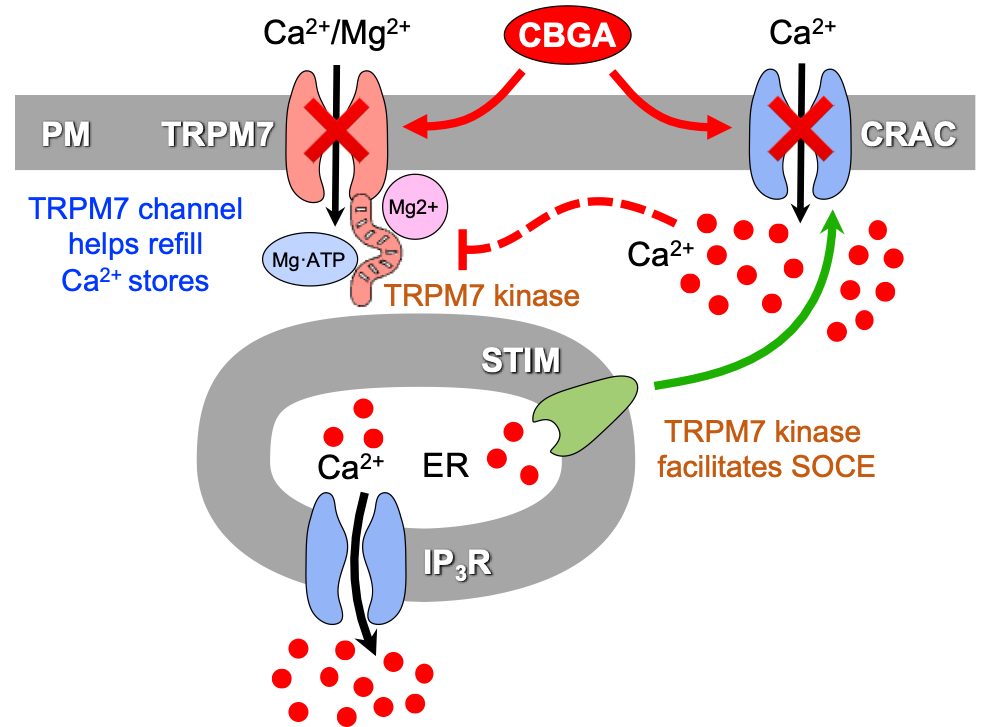
Dr. Suzuki’s study demonstrates that CBGA potently inhibits TRPM7 currents. Dr. Suzuki previously reported that CBGA has a potent inhibitory effect on both Store-Operated Calcium Entry (SOCE) via inhibition Calcium Release-Activated Calcium (CRAC) channels as well as the channel-kinase TRPM7. In this study, the authors comprehensively investigated the most common major and minor cannabinoids to determine their potential efficacy on TRPM7 channel function. They found that approximately half of the cannabinoids tested suppressed TRPM7 currents to some degree, with CBGA having the strongest inhibitory effect on TRPM7. The study found that the CBGA-mediated inhibition of TRPM7 requires a functional kinase domain, is sensitized by both intracellular Mg⋅ATP and free Mg2+, and reduced by increases in intracellular Ca2+. Finally, it demonstrates that CBGA inhibits native TRPM7 in B lymphocytes cell line. In conclusion, the study demonstrates that CBGA is the most potent cannabinoid in suppressing TRPM7 activity and possesses the potential to be a pharmacologic therapeutic for diseases in which TRPM7 is known to play an important role such as cancer, stroke, and kidney disease.